Blockchain Basics - Proof of Stake
In this blog post, we are going to talk about Proof of Stake or PoS. Proof of Stake is a relatively new technology, proposed by a user QuantumMechanic on the popular Bitcointalk.org forum for Bitcoin implementation. You can check the post here.
Currently, Cardano (ADA) is one of the most popular and widely used Proof of Stake blockchains. Although, it might not be long until Ethereum switches from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, which promises lower fees, better decentralization, and will lower environmental impact.
Proof of Stake, or PoS, is a blockchain protocol that validates transactions and protects the blockchain from 51% attacks. Its purpose is identical to the Proof of Work protocol.What is Proof of Stake?
Instead of workers (nodes) using computational power to validate transactions, consequently creating a negative impact on the environment with a lot of electricity used, Proof of Stake requires nodes to stake the balance. These nodes then validate the transactions.
How does Proof of Stake work?
As mentioned above, a Proof of Stake node validates transactions on the blockchain, but how exactly does it do it?
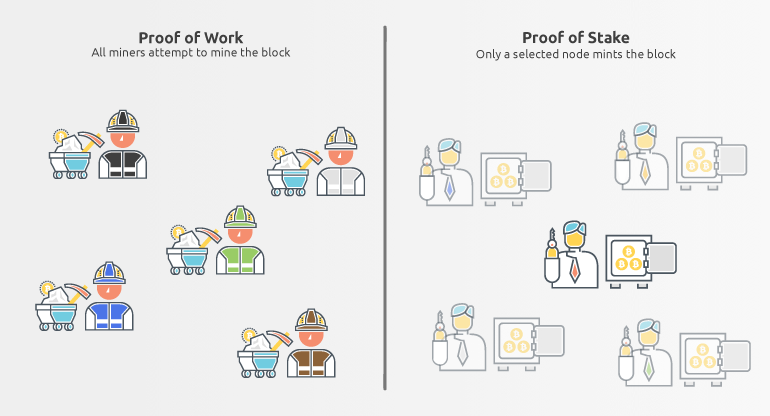
Proof of Stake does not have miners, but validators. Validators do not mine the blocks but mint (forge) them. Nodes become validators once they are randomly chosen by the network.
With Proof of Work, all miners work simultaneously, and the miner who solves the mathematical problem first will be rewarded with a block reward. This creates a lot of energy usage that could be avoided.
Proof of Stake network, on the other hand, picks only one node to become a validator and mint the block. Nodes are randomly chosen based on their staking age, staking amount, and other factors.
For a node to become a validator it must deposit a certain amount of coins into the network. This is called a stake. Ethereum's 2.0 minimum stake amount per node is currently 32 ETH. A stake acts as collateral. The higher the stake amount, the higher the odds of a node being chosen as a validator.
Because validators stake coins, we can trust them to validate the correct transactions in the block. If they were to dishonestly validate the transaction, they would lose a part or all of their stake.
Why Proof of Stake over Proof of Work?
Both PoS and PoW are essentially used to prevent double-spending on the blockchain. The only difference is in the methods that are used to prevent double-spending. The PoS method has some advantages compared to PoW. Proof of Stake was after all developed to solve the proof of work scalability, environment, and 51% attack problems.
The main Proof of Stake advantages are:
- Environmental footprint
- Decentralization
- Inflation
- Security
The most obvious is the negative environmental impact of PoW. Proof of Work currently uses an enormous amount of electricity to confirm the transactions. Proof of Stake on the other hand uses just a really small, practically neglectable, amount of electricity.
More people can join the staking as all they need is monetary value. With PoW, some miners can be only available to selected groups of people (early access ASICs).
Since PoS does not use high amounts of electricity, the block reward can be lowered, removed, or even have a negative block issuance (burning the fees). By creating a negative block reward (burning), the price of the currency should in theory, increase. Additionally, this way, the price could be controlled better and could cause less volatility.
Proof of Stake blockchains are more secure compared to Proof of Work blockchains.
Proof of Stake has its own advantages, but it also has a disadvantage:
- Money creates money
Rich validators will get richer as they will be picked more often. This risks a higher wealth concentration in the long run, hence the centralization of wealth in only a few nodes.







