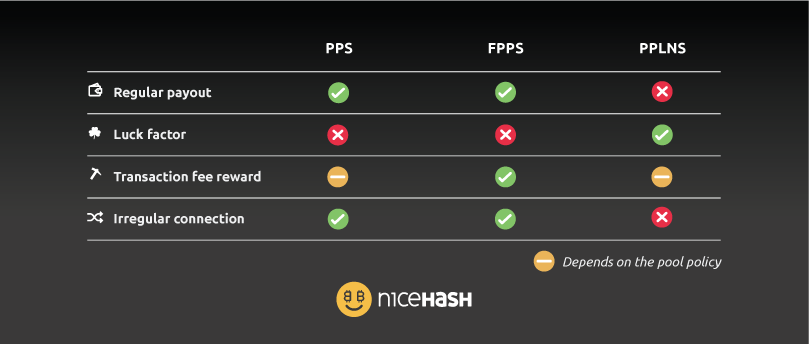
How mining pools distribute rewards? PPS vs FPPS vs PPLNS
When placing a new order on NiceHash hash-power Marketplace, you must be careful to pick the right pool that suits your order.
In this guide, we will take a look at different payment methods (or reward systems) provided by mining pools and how they could affect your profits.
There are many different payment methods available, but we are going to throw some light on the most common ones:
- PPS - Pay Per Share
- FPPS - Full Pay Per Share
- PPLNS - Pay Per Last (N)umber of Shares
Pay-Per-Share (PPS)
This payment method is pretty straightforward. You get paid for each valid share contributed. Each share is worth a certain amount of BTC or any other mineable cryptocurrency.
Share worth is calculated based on the probability of the number of shares needed for a pool to find a block. If the pool statistically needs to send 1000 valid shares to find one block or 12.5 BTC (at the moment of writing), then each share is worth 0.0125 BTC. As the network difficulty changes, the price for each share is changed too.
It is worth noting that you will always get paid with the PPS payment method, no matter if the pool finds a block or not. This means that the pool can lose money if the pool luck is low, or earn money if the pool luck is high. Statistically, pool luck should be around 100%. (higher percentage equals higher pool luck).
IDEAL ORDER FOR PPS: Low priced order for a longer period of time, which might not be mining constantly, but just when the price drops and attracts miners.
Full Pay-Per-Share (FPPS)
Full Pay-Per-Share or Pay-Per-Share Pus(PPS+) - these two are the same - they are very similar to ordinary Pay-Per-Share; the only difference is that the pool will also pay a transaction fee reward that is included if the block is found.
Typically when a pool finds a block, they split the BTC reward to the miners, but with the block reward, there also comes a transaction fee reward. This reward is collected by each transaction done on the blockchain (the fee you have to pay when making a transaction). With Full Pay-Per-Share, the pool will also pay the transaction fee rewards to the miners. For example, the Bitcoin block at depth 603308 had a fee reward of 0.49475167 BTC + 12.5 BTC block reward. (source: https://www.blockchain.com/btc/block/603308)
IDEAL ORDER FOR FPPS: Low priced order, which might not be mining constantly, but just when the price drops and attracts miners (lower price).
Pay-Per-Last N Shares (PPLNS)
Pay-Per-Last N Share system rewards miners only once the block has been found by the pool. This means that you will get paid only once the block has been found. Then the pool goes “back in time,” and checks for valid shares contributed before the winning block. This is called a time window. Miners get paid based on the valid shares that they have sent in that time window.
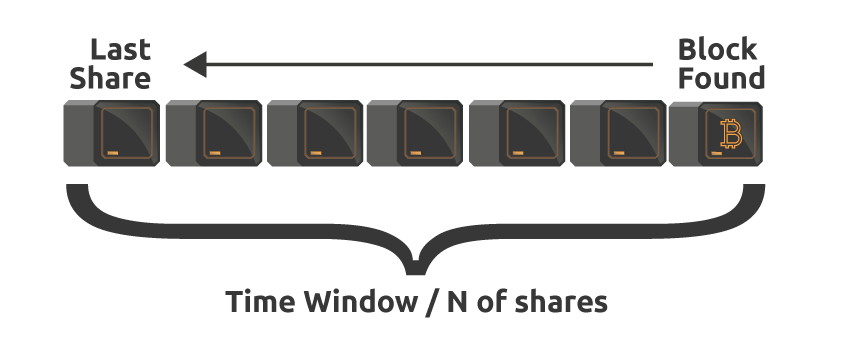
This method comes in handy for miners that do not hop from pool to pool and have a steady connection. Note that you may lose all your work (shares) if you disconnect from the pool before the block is found.
IDEAL ORDER FOR PPLNS: fix order on a big pool that has a high chance of finding a block within the order time limit. Or a standard order which will have miners connected for a longer time (at a higher price).
Conclusion
With the PPS and FPPS payment methods, you will get paid no matter if the pool finds a block or not. This is the most significant advantage over PPLNS. While on the other hand, PPLNS allows you to “gamble” in some way. If your order is sending hash power to a pool that happens to have a high block find at the time, you will most likely earn a lot more than on PPS or FPPS pool.